Welcome Thomas Kudla, Senior Software Engineer at Concepts NREC read more Kudla will develop and maintain AxCent®, the company’s flagship software product used for detailed 3D geometric design and...
This blog article is a follow up for the earlier blog “Coupled Optimization of Preliminary Design Geometry of Low Flow Steam Turbine with Curtis Stage Layout and Rankine Cycle Parameters”, which...
Designing turbines for low flow Rankine Cycle for steam is challenging due to their small size, manufacturing restrictions, clearances and cost constraints. Such turbines operate at significant...
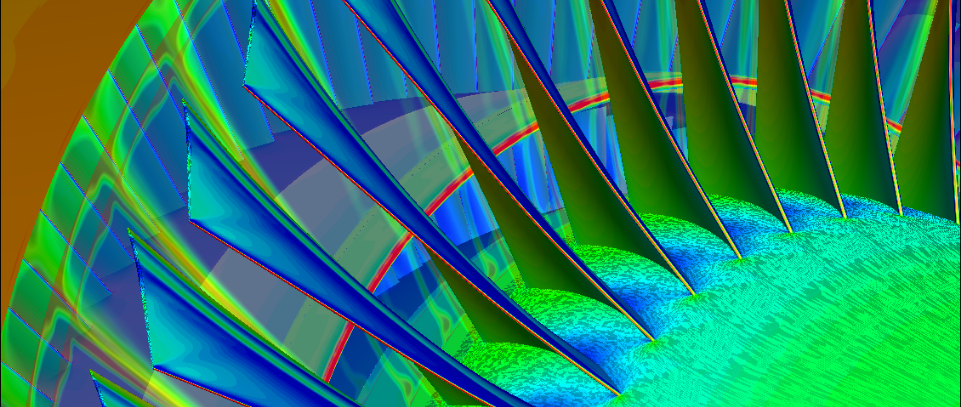
In many instances, the design of new turbofan engine is an iterative process of optimizing engine cycle parameters (i.e. thermodynamics) and executing preliminary design geometry of engine...
Frequently, there is a need to reconstruct 2D and 3D geometry from reported or measured surface data points. In most cases, the provided surface data include significant amounts of noise for various...
Many energy recovery, drive cycles (Organic and Steam Rankine cycles) and rocket propulsion cycles require the use of a turbine that operates at low volumetric flow and high-pressure ratio....
Many gas turbines with radial compressors utilize a radial-to-axial inlet duct upstream of the first compressor stage. Aside from the fact that flow in the duct generates aerodynamic losses, the flow...
High-efficiency, low-cavitation pumps often require a screw type inducer to treat the inflow to the main radial/mixed flow pump blades. Efficiency and head rise, split between inducer and main pump,...
New engine development is a costly endeavor and making the right decisions early in the engine design is extremely important. It requires multi-disciplinary consideration of the engine thermodynamic...
Arbitrary blade section profiling is an essential part of designing high performance axial turbines and compressors. In most cases such blade section models are formed by hybrid use of arbitrary...